An IPv6 multicast (one-to-many) address identifies a set of hosts. A packet with this type of address is delivered to all the hosts identified by that address. This type is similar to IPv4 multicast (Class D) addresses. IPv6 multicast addresses also supersede the broadcast function of IPv4 broadcasts; you use an “all-nodes” multicast address instead. One additional function of IPv6 multicast is to provide the IPv4 broadcast equivalent with the all-nodes multicast group.
For example, this IPv6 multicast address indicates the all-nodes address for interface-local scope:
FF01:0:0:0:0:0:0:1
And this IPv6 multicast address is the all-routers address for the local link:
FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:2
RFC 4291 specifies the format of IPv6 multicast addresses. As shown in Figure 2-6, the fields of the IPv6 multicast address are the FP, a value of 0xFF, followed by a 4-bit flags field, a 4-bit scope field, and 112 bits for the Group ID field. A quick way to recognize an IPv6 multicast address is that it begins with FF::/8.
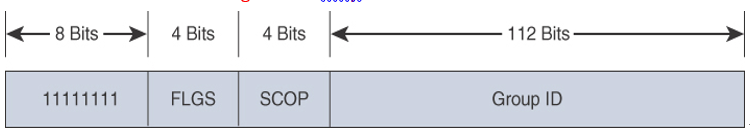
Figure 2-6 Multicast Address Format
The FLGS (flags) field consists of 0RPT.
The R flag R = 1 indicates a multicast address that embeds the address on the RP. R = 0 indicates a multicast address that does not embed the address of the RP.
If the P flag is 0, it indicates that a multicast address is not assigned based on the network prefix. If P=1, the multicast address is assigned based on the network prefix.
If T = 0, the address is a well-known multicast address assigned by IANA. If T = 1, the address is not a permanently assigned address.
The SCOP (scope) field limits the scope of the multicast group. Table 2-4 shows the assigned scope values.
Table 2-4 Multicast Scope Assignments
| SCOP (Binary) | SCOP (Hexadecimal) | Assignment |
| 0000 | 0 | Reserved |
| 0001 | 1 | Interface-local scope |
| 0010 | 2 | Link-local scope |
| 0011 | 3 | Reserved |
| 0100 | 4 | Admin-local scope |
| 0101 | 5 | Site-local scope |
| 0110 | 6 | Unassigned |
| 0111 | 7 | Unassigned |
| 1000 | 8 | Organization-local scope |
| 1001 | 9 | Unassigned |
| 1010 | A | Unassigned |
| 1011 | B | Unassigned |
| 1100 | C | Unassigned |
| 1101 | D | Unassigned |
| 1110 | E | Global scope |
| 1111 | F | Reserved |
The Group ID field identifies the multicast group within the given scope. The group ID is independent of the scope. A group ID of 0:0:0:0:0:0:1 identifies nodes, whereas a group ID of 0:0:0:0:0:0:2 identifies routers. Some well-known multicast addresses are listed in Table 2-5; they are associated with a variety of scope values.
Table 2-5 Well-Known IPv6 Multicast Addresses
| Multicast Address | Multicast Group |
| FF01::1 | All nodes (interface-local) |
| FF02::1 | All nodes (link-local) |
| FF01::2 | All routers (interface-local) |
| FF02::2 | All routers (link-local) |
| FF02::5 | Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) |
| FF02::6 | OSPFv3 designated routers |
| FF02::9 | Routing Information Protocol next generation (RIPng) |
| FF02::A | EIGRP routers |
| FF02::B | Mobile agents |
| FF02::C | DHCP servers/relay agents |
| FF02::D | All Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) routers |
| FF05::1 | All nodes in the local network site |
| FF0x::FB | Multicast DNS |
| FF02::1:2 | All DHCP and relay agents on the local network site (RFC 3313) |
| FF05::1:3 | All DHCP servers on the local network site (RFC 3313) |
Table 2-6 summarizes the IPv6 address types.
Table 2-6 IPv6 Address Types
| IPv6 Address Type | Description |
| Unicast | The IP address of an interface on a single host. It can be a source or destination address. |
| Anycast | An IP address that identifies a set of devices within an area. It can be only a destination address. |
| Multicast | An IP address that reaches a group of hosts identified by the address. It can be only a destination address. |
A CCNP enterprise designer should know how to identify address types based on the prefix. Table 2-7 summarizes the address types and their prefixes.
Table 2-7 IPv6 Address Prefixes
| IPv6 Address Type | Prefix |
| Loopback address | 0000::0001 |
| Unspecified address | 0000::0000 |
| Global unicast address | 2000::/3 |
| Unique local unicast | FC00::/7 |
| Link-local unicast address | FE80:/10 |
| Multicast address | FF00::/8 |
| OSPFv3 | FF02::5 |
| EIGRP routers | FF02::A |
| DHCP | FF02::C |




